Week 3 of #10Weeksofcloudops
Implement a 2-tier architecture in AWS using Terraform.
Terraform -
Terraform is an open source service that allows us to build infrastructure as a code to provision resources from any infrastructure provider. Terraform creates and manages resources on cloud platforms and other services through their application programming interfaces (APIs). Providers enable terraform to work with virtually any platform or service with an accessible API.
It lets us define resources and infrastructure in human-readable, declarative configuration files, rather than through a graphical user interface.
Prerequisites -
- AWS Account
- AWS CLI
- Terraform
- AWS Access key and Security Key.
- Microsoft Visual Studio code.
Creating providers.tf -
This defines a web application, including a Provider block, VPC with its networking components, Security block, Instances block (EC2 instance for Compute & RDS instance for database), an Application Load Balancer block and an Outputs block.
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.23"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.2.0"
}
provider "aws"{
region = "ap-south-1"
}
Creating variables.tf -
This file consists of input variables and by defining values to those variables, the end users can assign them to customize the configuration.
# custom VPC variable
variable "vpc_cidr" {
description = "custom vpc CIDR notation"
type = string
default = "10.0.0.0/16"
}
# public subnet 1 variable
variable "public_subnet1" {
description = "public subnet 1 CIDR notation"
type = string
default = "10.0.1.0/24"
}
# public subnet 2 variable
variable "public_subnet2" {
description = "public subnet 2 CIDR notation"
type = string
default = "10.0.2.0/24"
}
# private subnet 1 variable
variable "private_subnet1" {
description = "private subnet 1 CIDR notation"
type = string
default = "10.0.3.0/24"
}
# private subnet 2 variable
variable "private_subnet2" {
description = "private subnet 2 CIDR notation"
type = string
default = "10.0.4.0/24"
}
# AZ 1
variable "az1" {
description = "availability zone 1"
type = string
default = "us-east-1a"
}
# AZ 2
variable "az2" {
description = "availability zone 2"
type = string
default = "us-east-1b"
}
# ec2 instance ami for Linux
variable "ec2_instance_ami" {
description = "ec2 instance ami id"
type = string
default = "ami-090fa75af13c156b4"
}
# ec2 instance type
variable "ec2_instance_type" {
description = "ec2 instance type"
type = string
default = "t2.micro"
}
# db engine
variable "db_engine" {
description = "db engine"
type = string
default = "mysql"
}
# db engine version
variable "db_engine_version" {
description = "db engine version"
type = string
default = "5.7"
}
# db name
variable "db_name" {
description = "db name"
type = string
default = "my_db"
}
# db instance class
variable "db_instance_class" {
description = "db instance class"
type = string
default = "db.t2.micro"
}
# database username variable
variable "db_username" {
description = "database admin username"
type = string
sensitive = true
}
# database password variable
variable "db_password" {
description = "database admin password"
type = string
sensitive = true
}
Creating VPC.tf -
# creating VPC
resource "aws_vpc" "custom_vpc" {
cidr_block = var.vpc_cidr
tags = {
name = "custom_vpc"
}
}
Creating subnet.tf -
#Creating Subnets
# public subnet 1
resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet1" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
cidr_block = var.public_subnet1
availability_zone = var.az1
tags = {
name = "public_subnet1"
}
}
# public subnet 2
resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet2" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
cidr_block = var.public_subnet2
availability_zone = var.az2
tags = {
name = "public_subnet2"
}
}
# private subnet 1
resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet1" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
cidr_block = var.private_subnet1
availability_zone = var.az1
tags = {
name = "private_subnet1"
}
}
# private subnet 2
resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet2" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
cidr_block = var.private_subnet2
availability_zone = var.az2
tags = {
name = "private_subnet2"
}
}
Creating igw.tf (Internet Gateway) -
# creating internet gateway
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "igw" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
tags = {
name = "igw"
}
}
Creating route_table.tf (Routing Tables) -
# creating route table
resource "aws_route_table" "rt" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.igw.id
}
tags = {
name = "rt"
}
}
Associating Route Tables with Subnets -
Creating routetable_assciation_subnettf
# tags are not allowed here
# associate route table to the public subnet 1
resource "aws_route_table_association" "public_rt1" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet1.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.rt.id
}
# associate route table to the public subnet 2
resource "aws_route_table_association" "public_rt2" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet2.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.rt.id
}
# associate route table to the private subnet 1
resource "aws_route_table_association" "private_rt1" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.private_subnet1.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.rt.id
}
# associate route table to the private subnet 2
resource "aws_route_table_association" "private_rt2" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.private_subnet2.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.rt.id
}
Creating Security Groups -
Creating sg.tf -
# SECURITY BLOCK
# create security groups for vpc (web_sg), webserver, and database
# custom vpc security group
resource "aws_security_group" "web_sg" {
name = "web_sg"
description = "allow inbound HTTP traffic"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
# HTTP from vpc
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
# outbound rules
# internet access to anywhere
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
name = "web_sg"
}
}
# web tier security group
resource "aws_security_group" "webserver_sg" {
name = "webserver_sg"
description = "allow inbound traffic from ALB"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
# allow inbound traffic from web
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
security_groups = [aws_security_group.web_sg.id]
}
egress {
from_port = "0"
to_port = "0"
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
name = "webserver_sg"
}
}
# database security group
resource "aws_security_group" "database_sg" {
name = "database_sg"
description = "allow inbound traffic from ALB"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
# allow traffic from ALB
ingress {
from_port = 3306
to_port = 3306
protocol = "tcp"
security_groups = [aws_security_group.webserver_sg.id]
}
egress {
from_port = 32768
to_port = 65535
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
name = "database_sg"
}
}
Creating Instances and RDS -
Creating ec2_rds.tf -
This creates EC2 instances in the public subnets as “web tier” & RDS instance within the private subnet for “database tier”
# INSTANCES BLOCK - EC2 and DATABASE
# user_data = file("install_apache.sh")
# if used with file option - get multi-line argument error
# as echo statement is long
# 1st ec2 instance on public subnet 1
resource "aws_instance" "ec2_1" {
ami = var.ec2_instance_ami
instance_type = var.ec2_instance_type
availability_zone = var.az1
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet1.id
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.webserver_sg.id]
user_data = <<EOF
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
EC2AZ=$(curl -s http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/placement/availability-zone)
echo '<center><h1>This Amazon EC2 instance is located in Availability Zone:AZID </h1></center>' > /var/www/html/index.txt
sed"s/AZID/$EC2AZ/" /var/www/html/index.txt > /var/www/html/index.html
EOF
tags = {
name = "ec2_1"
}
}
# 2nd ec2 instance on public subnet 2
resource "aws_instance" "ec2_2" {
ami = var.ec2_instance_ami
instance_type = var.ec2_instance_type
availability_zone = var.az2
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet2.id
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.webserver_sg.id]
user_data = <<EOF
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
EC2AZ=$(curl -s http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/placement/availability-zone)
echo '<center><h1>This Amazon EC2 instance is located in Availability Zone:AZID </h1></center>' > /var/www/html/index.txt
sed"s/AZID/$EC2AZ/" /var/www/html/index.txt > /var/www/html/index.html
EOF
tags = {
name = "ec2_2"
}
}
# Database subnet group
resource "aws_db_subnet_group" "db_subnet" {
name = "private_subnet"
subnet_ids = [aws_subnet.private_subnet1.id, aws_subnet.private_subnet2.id]
}
# Create database instance
resource "aws_db_instance" "my_db" {
allocated_storage = 5
engine = "mysql"
engine_version = "5.7"
instance_class = "db.t2.micro"
identifier = "db-instance"
db_name = "sqldatabase"
username = "admin"
password = "password"
db_subnet_group_name = aws_db_subnet_group.db_subnet.id
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.webserver_sg.id]
publicly_accessible = false
skip_final_snapshot = true
multi_az = true
}Creating Application Load Balancer -
Creating alb.tf -
# ALB BLOCK
# alb target group
resource "aws_lb_target_group" "external_target_g" {
name = "external-target-group"
port = 80
protocol = "HTTP"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.custom_vpc.id
}
resource "aws_lb_target_group_attachment" "ec2_1_target_g" {
target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.external_target_g.arn
target_id = aws_instance.ec2_1.id
port = 80
}
resource "aws_lb_target_group_attachment" "ec2_2_target_g" {
target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.external_target_g.arn
target_id = aws_instance.ec2_2.id
port = 80
}
# ALB
resource "aws_lb" "external_alb" {
name = "external-ALB"
internal = false
load_balancer_type = "application"
security_groups = [aws_security_group.web_sg.id]
subnets = [aws_subnet.public_subnet1.id,aws_subnet.public_subnet2.id]
tags = {
name = "external-ALB"
}
}
# create ALB listener
resource "aws_lb_listener" "alb_listener" {
load_balancer_arn = aws_lb.external_alb.arn
port = "80"
protocol = "HTTP"
default_action {
type = "forward"
target_group_arn = aws_lb_target_group.external_target_g.arn
}
}
Creating outputs.tf -
This file contains the definitions for the output values of the resources.
# OUTPUTS
# get the DNS of the load balancer
output "alb_dns_name" {
description = "DNS name of the load balancer"
value = "${aws_lb.external_alb.dns_name}"
}
output "db_connect_string" {
description = "MyRDS database connection string"
value = "server=${aws_db_instance.my_db.address}; database=ExampleDB; Uid=${var.db_username}; Pwd=${var.db_password}"
sensitive = true
}
After all the terraform files are ready. We can start deploying.
As already mentioned, the access key and security key were created and the same was used for the authentication.
Now we can start with the terraform commands -
1. terraform init - This code basically prepares the current working directory for terraform to run the configurations.
3. terraform plan - This basically shows a plan for every resource that is to be executed/deployed. It allows us to review the plan before executing the configuration.
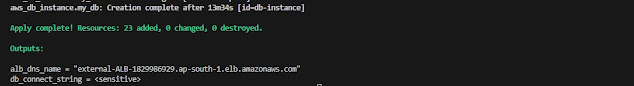
4.terraform apply - terraform apply executes the terraform files in the directory and creates the resources.
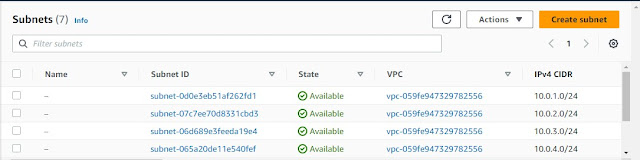
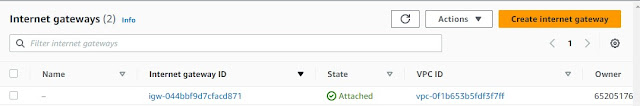
We can also verify all the resources by logging into AWS Management Concole and verify -
VPC -
Subnets -
Internet Gateway -
EC2 Instances -
RDS -
After verifying all the resources are created. We can destroy the resources.
terraform destroy - terraform destroy command destroys all the resources which were created.
You can find all the files in the github link below -
.jpg)










.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment